DIAlog AI: Part Four: Behind the Green Screen: Is it time to Pull the CORD-19 on CT-BERTie the Bus's Q&A? CT=Clinical-Trial & Covid-Twitter & Conspiracy-Theory
DIAl-a-Docs Dirty Dozen 10 to 12: CT-BERTie & CO went OS at Warp Speed for CO-V-ID. CO-Author of Modelling Interventions & Geo-tags with Emer's Prestigious Paris Pill Dispenser from 1 Step to 1 Health
Dial-a-Docs 10) Alphabetical A2I Descent through Time to the Origin-Al BERT. From current CO-V-ID CONstraint Open Source COpies to ‘Google AI Language’ coming out as BERT Q&A pre-trained & CO-dependant on the COrpus.
A) PRESENTED NOV 2022 UK Clinical Trial BERT.
Eva-Lisa Meldau, Data Scientist Uppsala Monitoring Centre social media post was from the ‘International Society of Pharmacovigilance’ (ISOP) Boston Seminar Nov 2022 re: Intelligent Automation in Pharmacovigilance, Safety monitoring and signal detection for the novel COVID-19 vaccines.:
Automated redaction of narratives from the UK Yellow Card Scheme using BERT
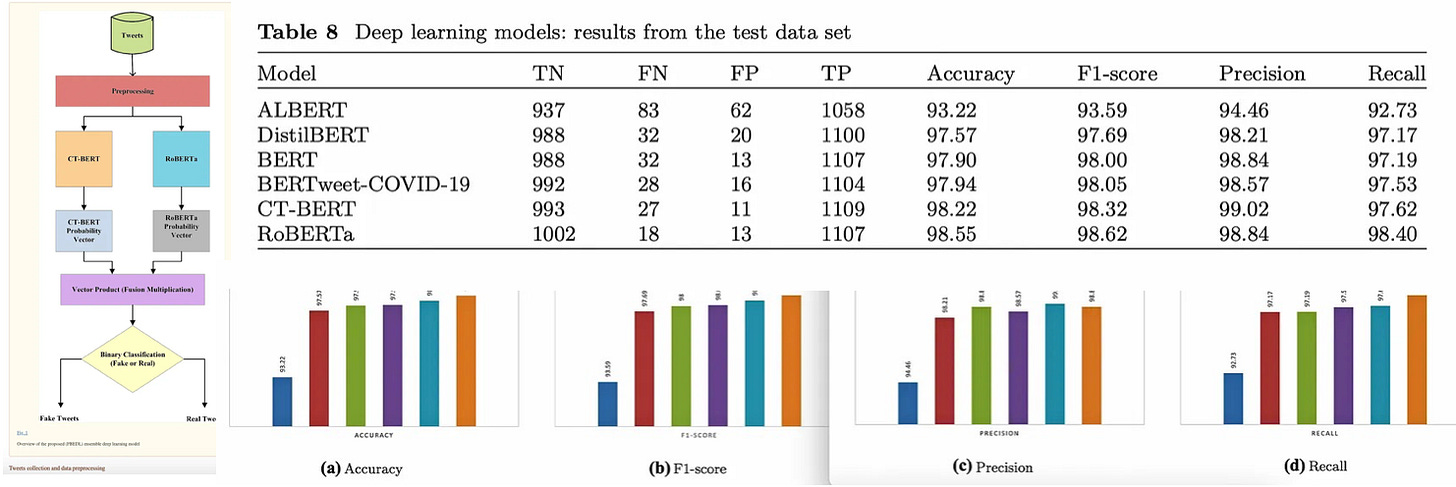
B) Published JAN 2022 Received OCT 2021. Fake or real news about COVID-19? Pretrained transformer model to detect potential misleading news.
‘Fake or real news about COVID-19? Pretrained transformer model to detect potential misleading news.’:1
The primary goal of this paper is to educate society about the importance of accurate information and prevent the spread of fake information.:
Categorize given tweets as either fake or real news.
Tested various deep learning models on the ‘COVID-19 fake dataset’. The CT-BERT and RoBERTa deep learning models outperformed other deep learning models like BERT, BERTweet, AlBERT, and DistlBERT.
Fake news COVID-19 dataset:
From the COVID-19 outbreak (2020), Constraint@AAAI 2021 workshop organizers provided the COVID-19 fake news English dataset with the id, tweet, label (“Fake” and “Real”). These were collected from tweets, instagram posts, facebook posts, press releases, or any other popular media content. Using the Twitter API, real news was gathered from potential real tweets.:
Official accounts such as the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the World Health Organization (WHO), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Covid India Seva, and others may have real tweets.
They give valuable COVID-19 information such as vaccine progress, dates, hotspots, government policies, and so on.
The study demonstrated how to use a novel NLP application:
To detect real or fake COVID-19 tweets to assist individuals in avoiding hysteria about COVID-19 tweets and improvement of COVID-19 therapies and public health measures.
C) Submitted DEC 2020 g2tmn at Constraint@AAAI2021: Exploiting CT-BERT and Ensembling Learning for COVID-19 Fake News Detection.
This paper presents the results for the Constraint@AAAI2021 Shared Task: COVID-19 Fake News Detection in English2 using the transformer-based ensemble of COVID-Twitter-BERT (CT-BERT) models. Models used [determine] the ways of text preprocessing and adding extra data. The best model achieved the weighted F1-score of 98.69 on the test set (the first place in the leaderboard) of this shared task that attracted 166 submitted teams.
D) CONSTRAINT 2021 First Workshop on Combating Online Hostile Posts in Regional Languages during Emergency Situation Collocated with AAAI.
SHARED TASK ‘CONSTRAINT 2021’3 ‘COVID19 Fake News Detection in English’:4
This subtask focused on the detection of COVID-19-related fake news in English. The sources of data were various social-media platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, etc.:
Given a social media post, the objective of the shared task was to classify it into either fake or real news. For example, the following two posts belong to fake and real categories, respectively.
If you take Crocin thrice a day you are safe.FakeWearing mask can protect you from the virusReal
E) Submitted NOV 2020 ‘Fighting an Infodemic: COVID-19 Fake News Dataset’.
‘Fighting an Infodemic: COVID-19 Fake News Dataset’:5
Real - Tweets from verified sources and give useful information on COVID-19.
Fake - Tweets, posts, articles which make claims and speculations about COVID-19 which are verified to be not true.
Fake news data from public fact- verification websites and social media.:
Facebook posts, tweets, a news piece, Instragram posts, public statements, press releases, or any other popular media content, are leveraged towards collecting fake news.
Besides these, popular fact-verification websites like PolitiFact, Snopes 8, Boomlive are also used as they play a crucial role towards collating the manually adjudicated details of the veracity of the claims becoming viral. These websites host COVID-19 and other generic topic related verdicts.
The factually verified (fake) content can be easily found from such websites.
Real News crawl tweets from official and verified twitter handles of the relevant sources using twitter API.:
The relevant sources are the official government accounts, medical institutes, news channels, etc. We collect tweets from 14 such sources, e.g., World Health Organization (WHO), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Covid India Seva, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), etc.
F) Submitted SEP 2021 Clinical Trial Information Extraction with BERT.
‘Clinical Trial Information Extraction with BERT’6 was presented at ‘Health NLP 2021, IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI 2021)’ by Novartis:
Natural language processing (NLP) of clinical trial documents can be useful in new trial design. Here we identify entity types relevant to clinical trial design and propose a framework called CT-BERT for information extraction from clinical trial text. We trained named entity recognition (NER) models to extract eligibility criteria entities by fine-tuning a set of pre-trained BERT models. We then compared the performance of CT-BERT with recent baseline methods including attention-based BiLSTM and Criteria2Query.
The results demonstrate the superiority of CT-BERT in clinical trial NLP.
This study introduced a new framework CT-BERT and trained NER models to leverage BERT-based modelling for clinical trial information extraction. Studied how pre-trained BERT models may impact the NER performance. Collectively, CT-BERT shows significant improvement in model quality.:
Getting high accuracy in information extraction paves the way for automatic AI-driven clinical trial design.
G) Submitted JUNE 2021 COBERT: COVID-19 Question Answering System Using BERT.
‘COVID-19 Question Answering System Using BERT’7 Abstract:
The risks are most certainly not trivial, as decisions made on fallacious, answers may endanger trust or general well being and security of the public. But, with thousands of research papers being dispensed on the topic, making it more difficult to keep track of the latest research.
Proposed COBERT:
A retriever-reader dual algorithmic system that answers the complex queries by searching a document of 59K corona virus-related literature made accessible through the Coronavirus Open Research Dataset Challenge (CORD-19).
The retriever is composed of a TF-IDF vectorizer capturing the top 500 documents with optimal scores.
The reader which is pre-trained Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) on SQuAD 1.1 dev dataset built on top of the HuggingFace BERT transformers, refines the sentences from the filtered documents, which are then passed into ranker which compares the logits scores to produce a short answer, title of the paper and source article of extraction.
BERT: stands for ‘Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformer’ the most recent refinement of a series of neural models that make substantial use of pretraining, and has prompted noteworthy gains in numerous natural language processing tasks, going from a text classification to do tasks like question answering from the corpus.
Distil BERT: is a BERT based cheap, small, fast, and light Transformer model, English language model, pre-trained on the same data used to pre-trained BERT.:
Concatenation of the Toronto Book Corpus and full English Wikipedia.
Using distillation with the supervision of the Bert-base-uncased version of Bert. The model has 6 layers, 768 dimensions, and 12 heads, totalizing 66M parameters.:
Ranker: presents the top 3 answers based on a weighted score between the retriever score and reader score (based on DistilBERT QA Q-A pair probability).
Cosine similarity (cos(𝑞⃗ ,𝑑⃗ )), helps to find the similarity among two vectors of inner product space and conclude whether these vectors are indicating in the same direction. We frequently calculate the similarity of documents in tasks such as text analysis.
Experimental Setup Dataset:
COBERT system uses the dataset of CORD-19: ‘COVID Open Research Data’ set collected by The White House, with the help of leading research groups like Allen Institute for AI and Kaggle.
The dataset consists of a collection of work of several Researchers and its analysis. It consists of around 59 thousand papers and around 41 thousand full texts incorporating papers distributed in more than 3200 journals. Many texts are related to institutions situated in the United States (over 16 thousand papers) followed by the United Kingdom (over 3 thousand papers) and the European Union and then Asian countries.:
Chinese organizations have seen a brilliant ascent this year (over 5K papers) because of China’s status as the principal focal point of the COVID-19 episode, thus, making the source of data very much diverse.
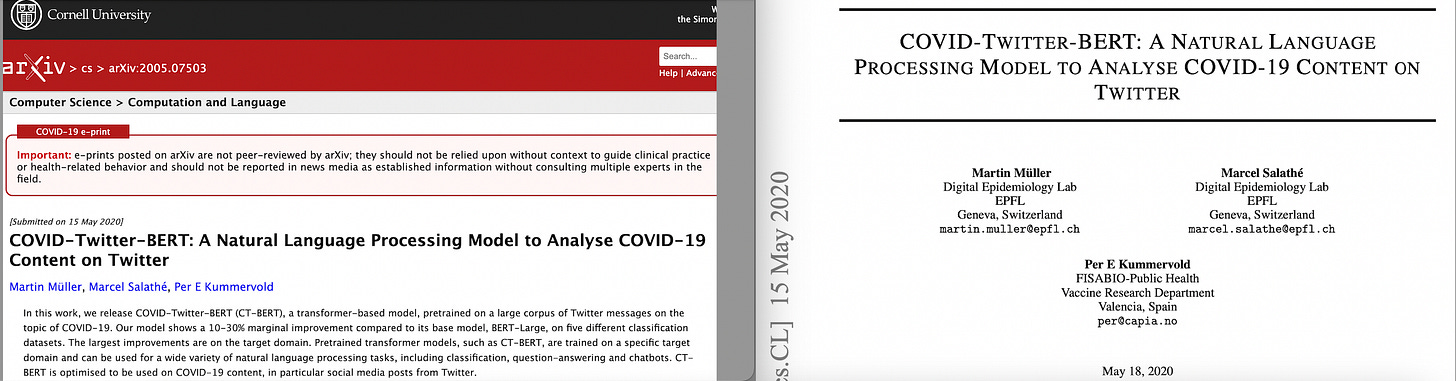
H) Submitted MAY 2020 COVID-Twitter-BERT: A Natural Language Processing Model to Analyse COVID-19 Content on Twitter.
2020 May ‘COVID-TWITTER-BERT: A Natural Language Processing Model to Analyse COVID-19 Content on Twitter’ by Marcel Salathé et al’8
Marcel Salathes’ ‘Digital Epidemiology Lab’ at the ‘École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne’ (EPFL) has a Github page for the study. The Readme for COVID-TWITTER-BERT9 explains:
COVID-Twitter-BERT (CT-BERT) is a transformer-based model pretrained on a large corpus of Twitter messages on the topic of COVID-19.
CT-BERT [finetuned using Huggingface] is reported as having a 10-30% marginal improvement compared to its base model, BERT-Large with the largest improvements on the ‘target domain’. Pretrained transformer models, such as CT-BERT, are trained on a specific ‘target domain’ and can be used for a wide variety of natural language processing tasks, including classification, question-answering and chatbots.:
CT-BERT is optimised to be used on COVID-19 content, in particular social media posts from Twitter.
The CT-BERT model is trained on a corpus of 160M tweets about the coronavirus collected through the Crowdbreaks platform during the period from January 12 to April 16, 2020. Crowdbreaks uses the Twitter filter stream API to listen to a set of COVID-19-related keywords in the English language.
Prior to training, the original corpus was cleaned for retweet tags. Each tweet was pseudonymised by replacing all Twitter usernames with a common text token. A similar procedure was performed on all URLs to web pages.
‘Digital Epidemiology Lab Github CrowdBreaks Welcome’10 Goal:
For many health-related issues human behaviour is of central importance for Public Health to design appropriate policies. Health behaviors are partially influenced by people's opinion which has been traditionally assessed in surveys. Social media can be used to complement traditional surveys and serve as a low-cost, global, and real-time addition to the toolset of Public Health surveillance.
Past & ongoing Crowdbreaks projects:
Vaccine sentiment tracking.
Assessing public opinion on CRISPR/Cas9.
Github crowdAI (www.crowdAI.org) is also developed by scientists and engineers at EPFL in Switzerland. CrowdAI is a not-for-profit platform open to participants from anywhere in the world for ‘open data’ challenges. It has two goals: to be the place for
-Solving (big) data problems in open science through open challenges.
-Learning about the techniques used to solve these problems.
I) Submitted OCT 2018: BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding ‘Google AI Language’.
The birth of BERT by ‘Google AI Language’11:
We introduce a new language representation model called BERT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. Unlike recent language representation models (Peters et al., 2018a; Radford et al., 2018), BERT is designed to pretrain deep bidirectional representations from unlabeled text by jointly conditioning on both left and right context in all layers. As a result, the pre-trained BERT model can be fine tuned with just one additional output layer to create state-of-the-art models for a wide range of tasks, such as question answering and language inference, without substantial task specific architecture modifications.
Dial-a-Docs 11A) A CT-BERT Author Citations geo-tagged with Emer's Prestigious Paris Pill Dispenser (TB / AMR) at the home of the Particle Accelerator. To school / lead us on ‘Life Sciences’ & ‘Computer & Comms Sciences’ in: [Lab + Epidemiology + Digital].
‘A Pigeon Poo-generated Pic & Word Chrono-Cloud thingee’ with the 2016 ‘Statistical physics of vaccination’12 prominent from querying the ePrints of ‘Digital Epidermology Lab’ Crowdbreaks / CT-BERT / AI Author, Marcel Salathé & github owner of a ‘best pizza’ community project with ‘Comet Ping Pong’ in Washington DC listed.:
Where is the best pizza in a given city? This is a community project. Pull requests accepted and I will totally make you a collaborator—if you ask and you’re not some kind of deep-dish-eating monster.
DIAl-a-Docs 11 B) CT-BERTie the Bus Fuel Depot [Convergence]. Real World Data, Cable & Corpus Linkages to both Catholic Ascension Hospital Chain & Darwin’s Descension on an Isle with the weirdest set of random coincidences. Q/ Who Wrote this Script Again? A/
A L P H A B E T
where:
A is for Ascension Health System
On 18th November 2019 Tech Target report:
Google-Ascension deal reveals murky side of sharing health data: The Google-Ascension partnership is a 'PR failure' that demonstrates a need for greater transparency about what happens to patient health data.
Ascension, a Catholic health system based in St. Louis, partnered with Google to transition the health system's infrastructure to the Google Cloud Platform, to use the Google G Suite productivity and collaboration tools, and to explore the tech giant's artificial intelligence and machine learning applications.
By doing so, it is giving Google access to patient data, which the search giant can use to inform its own products.
L is for Lives of Patients
On November 13th 2019 Ascension report on Technology that improves patients’ lives and caregivers’ experience.:
The ‘secret’ code name for planning purposes, Ascension and Google named our collaboration Project Nightingale as a shorthand way of referring to it. The name reflects the work of Florence Nightingale, a trailblazing figure in nursing who greatly affected 19th- and 20th-century policies around proper care.
Ascension’s clinical data, hosted in the Google Cloud Platform, is housed within an Ascension-owned virtual private space. Google is not permitted to use the data for marketing or research purposes.:
Hospitals and clinical software vendors across the country have converted or are in the process of converting to electronic health records stored in the cloud and soon the entire industry will be adopting this approach.
All of Google’s work with Ascension is in compliance with applicable regulations, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and is covered by a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) that governs Protected Health Information (PHI).:
Artificial intelligence/machine learning will help provide insights, with a licensed clinician always making the final treatment decisions.
Last year, we provided $2 billion in care of persons living in poverty and other community benefit programs.
We selected Google to help us on our journey of transformation. As a Catholic health ministry, we conducted an Ethics Review to ensure this collaboration is aligned with our Mission and Values, and that it is consistent with our Catholic identity.
P is for Portugal Branching Unit
On November 15, 2019 Google Submarine Global Network Infrastructure Strategy blogs ‘Curie subsea cable set to transmit to Chile, with a pit stop to Panama’.:
Once again, we’re reminded that the cloud isn’t in the sky—it’s in the ocean.
On June 29, 2019 the same Google cloud blog reports ‘Introducing Equiano, a subsea cable from Portugal to South Africa’:
Because Equiano is fully funded by Google, we’re able to expedite our construction timeline and optimize the number of negotiating parties. First phase of the project, connecting South Africa with Portugal, is expected to be completed in 2021.
Between 2016 and 2018, Google invested US$47 billion in capex.
Acension Island history of the Atlantic Cable & Undersea Communications from the first submarine cable of 1850 to the worldwide fiber optic network is explained here by Bill Glover.
H is for (St) Helena
On 1st September 2021 St Helena reports ‘Fibre Optic Cable Landed on St Helena St Helena Govt (SHG)’:
Sunday, 29 August 2021, was a ground-breaking day in St Helena’s digital history as the Island’s branch of the Equiano Subsea Cable was landed here.
Acknowledges the €21.5 million allocated by the EU under the EDF’11 programme to the territory, of which St Helena received around €17 million to support the delivery of the SHG Digital Strategy and to achieve the goals of the 10 Year Plan.:
Driving the Island forward in the digital age.
The high-speed fibre cable should offer opportunities for private sector development, distance learning, tele-medicine and e-commerce.
Notes to Editors: In December 2019, SHG signed a contract with Google to connect St Helena Island to the Equiano Subsea Fibre Optic Cable, delivering St Helena’s first high-speed, fibre-optic connectivity.
‘Preparing for Our digital destiny’ - a Chevening Alumni Project.:
A is for Ascension Island
Ascension Island Government, like other Overseas Territories and the Crown Territories, is not part of the United Kingdom.:
It has its own Constitution (shared with St Helena and Tristan da Cunha), is internally self-governing, makes its own laws, has a separate fiscal jurisdiction and has tax raising powers through the Governor. The United Kingdom is responsible for the defence, international relations, and internal security of the territory.
B is for Botanist (Darwin)
In this BBC news article on Ascension, ‘The island where nothing makes sense’ it says Darwin discussed how to make Ascension more habitable for humans with his friend Joseph Hooker, later director of the Royal Botanic Gardens at Kew, who visited in 1843. Hooker devised a plan.:
Hooker, to his credit, knew his planting scheme would push out the endemic ferns. What he perhaps didn't realise was just how much havoc it would cause.
The Darwin Initiative Lead Organisation is the Government of Ascension - AIGCD (Ascension Island Government Conservation Department).:
The Darwin Initiative is a UK govt grants scheme that helps protect biodiversity, the natural environment and the local communities that live alongside it in developing countries, building environmental knowledge, capacity building., research & implementing international biodiversity agreements.
E is for Earth Summit
The Darwin Iniative was announced by the UK Government at the Rio Earth Summit in 1992. Since awarded over £164M to more than 1,143 projects across 159 countries.:
Supports developing countries to conserve biodiversity and reduce poverty.
T is for Trade &or Treaty
The Darwin Initiative provides grants to meet their objectives under: the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (ITPGRFA), the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit-Sharing (ABS).
Funded by Defra (Food & Rural Affairs), DFID (Int. Dev.) and FCO (Foreign & Commonwealth Office) in the UK. Expert cttee members include conservationists from University of Oxford and UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC).:
The Darwin Expert Committee consists of experts from government, academia, science and the private sector.
Dial-a-docs 12) BERTie & Fren’s I/Os, Replications & Bias's are COnstrained by the Fat Controller COmmand via the COrpus. Why did BERTie & Co go Visibly Bananas WarpSpeed Style for CO-V-ID?
Tech Crunch March 16 2020 reports in a briefing on Monday, research leaders across tech, academia and the government joined the White House to announce an open dataset full of scientific literature on the novel coronavirus.
This ‘COVID-19 Open Research Dataset’ or CORD-19 involved the
Semantic Scholar team at the Allen Institute for AI partnering with leading research groups to provide CORD-19, a free resource of more than 280,000 scholarly articles about the novel coronavirus for use by the global research community.
The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative Head of Science, Cori Bargmann, said of the project:
Sharing vital information across scientific and medical communities is key to accelerating our ability to respond to the coronavirus pandemic.
The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative:
Hopes that the global machine learning community will be able to help the science community connect the dots on some of the enduring mysteries about the novel coronavirus as scientests pursue knowledge around prevention, treatment and a vaccine.
Tech Crunch said at the time the CORD-19 data set announcement was certain to roll out more smoothly than the White House’s last attempt at a coronavirus-related partnership with the tech industry. The White House had come under criticism the week before for President Trump’s announcement that:
Google would build a dedicated website for COVID-19 screening.
In fact, the site was [already] in development by Verily, Alphabet’s life science research group, and intended to serve California residents, beginning with San Mateo and Santa Clara County.
(A L P H A B E T is the parent company of Google).
‘Towards Data Science’ on March 18 2020 reports ‘Kaggle Released CORD-19 — an AI Challenge on the COVID-19’:
To address the [COVID-19] problem, researchers and leaders from the leading AI institutes, including Allen Institute for AI and Microsoft, and the federal government agency (i.e., the National Library of Medicine) have teamed together with extensive collaboration, resulting in the release of the COVID-19 Open Research Dataset (CORD-19) of scholarly literature about COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, and other kinds of coronavirus.
COVID-19 Open Research Dataset Challenge (CORD-19): An AI challenge with AI2, CZI, MSR, Georgetown, NIH & The White House:13
This dataset was created by the Allen Institute for AI in partnership with the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, Georgetown University’s Center for Security and Emerging Technology, Microsoft Research, IBM, and the National Library of Medicine - National Institutes of Health, in coordination with The White House Office of Science and Technology Policy.
A resource of over 1,000,000 scholarly articles, including over 400,000 with full text, about COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, and related coronaviruses. This freely available dataset is provided to the global research community to apply recent advances in natural language processing and other AI techniques to generate new insights in support of the ongoing fight against this infectious disease.
A list of the initial key questions can be found under the Tasks section of this dataset. These key scientific questions were drawn from the NASEM’s SCIED (National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine’s Standing Committee on Emerging Infectious Diseases and 21st Century Health Threats) research topics and the World Health Organization’s R&D Blueprint for COVID-19.:
Many of these questions are suitable for text mining, and we encourage researchers to develop text mining tools to provide insights on these questions.
2022 Jan 13 ‘Fake or real news about COVID-19? Pretrained transformer model to detect potential misleading news’
SreeJagadeesh Malla, P J A Alphonse
Department of Computer Applications, National Institute of Technology, Thuvakudi, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu 620015 India
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8756170/
2021 Jan 13 ‘g2tmn at Constraint@AAAI2021: Exploiting CT-BERT and Ensembling Learning for COVID-19 Fake News Detection’
Anna Glazkova * Timofey Trifonov University of Tyumen, ul. Volodarskogo 6, 625003 Tyumen, Russia
Maksim Glazkov, Organization of cognitive associative systems LLC, ul. Gertsena 64, 625000 Tyumen, Russia
https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.11967v3
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2012.11967v3
2021 Feb 8 ‘CONSTRAINT 2021’ Collocated with AAAI 2021
Keynote, Shared Tasks, Accepted Papers etc.
https://web.archive.org/web/20221130043920/https://www.lcs2.in/CONSTRAINT-2021/
2021 Feb 8 SHARED TASK CONSTRAINT 2021, GitHub
First Workshop on Combating Online Hostile Posts in Regional Languages during Emergency Situation Collocated with AAAI 2021
https://web.archive.org/web/20220216200158/https://constraint-shared-task-2021.github.io
2020 Nov 6 ‘Fighting an Infodemic: COVID-19 Fake News Dataset’
Parth Patwa, Shivam Sharma, Srinivas Pykl, Vineeth Guptha, Gitanjali Kumari, Md Shad Akhtar, Asif Ekbal, Amitava Das, Tanmoy Chakraborty
§IIIT Sri City, India. †IIIT Delhi, India ‡IIT Patna, India. *Wipro Reseach, India
https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.03327
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2011.03327
2021 Sep 11 ‘Clinical Trial Information Extraction with BERT’
Xiong Liu, Greg L. Hersch , Iya Khalil, Murthy Devarakonda Data Science and AI, Novartis, Cambridge, MA, USA
Greg L. Hersch Global Drug Development, Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland
https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.10027
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2110.10027
2021 Jun 26 COBERT: COVID-19 Question Answering System Using BERT
Jafar A Alzubi 1, Rachna Jain 2, Anubhav Singh 2, Pritee Parwekar 3, Meenu Gupta 4
1Al-Balqa Applied University, Salt, Jordan
2Bharati Vidyapeeth’s College of Engineering, New Delhi, India
3SRM Institute of Science and Technology, NCR Campus, Ghaziabad, India
4Chandigarh University, Ajitgarh, Punjab India
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8220121/
2020 May 15 COVID-TWITTER-BERT: A NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING MODEL TO ANALYSE COVID-19 CONTENT ON TWITTER
Martin Müller Digital Epidemiology Lab EPFL Geneva, Switzerland
Marcel Salathé Digital Epidemiology Lab EPFL Geneva, Switzerland
Per E Kummervold FISABIO-Public Health Vaccine Research Department Valencia, Spain
https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.07503
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.07503
COVID-Twitter-BERT Readme
Github Site of ‘Digital Epidemiology Lab, EPFL
Station 19 CH-1015 Lausanne Switzerland
https://web.archive.org/web/20221204012043/https://github.com/digitalepidemiologylab/covid-twitter-bert
Crowdbreaks Welcome
Github Site of ‘Digital Epidemiology Lab, EPFL
Station 19 CH-1015 Lausanne Switzerland
https://web.archive.org/web/20230603223429/https://github.com/digitalepidemiologylab/crowdbreaks-welcome
2019 May 24 ‘BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding’
Jacob Devlin Ming-Wei Chang Kenton Le
Google AI Language.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.04805
Seacch where author = Salathe Marcel
https://arxiv.org/search/?query=Salathe+Marcel&searchtype=author&abstracts=show&order=-announced_date_first&size=50
NOV 2016: Statistical Physics of Vaccination
Zhen Wang a , Chris T. Bauch b, Samit Bhattacharyya c, Alberto d’Onofrio d , Piero Manfredi e , Matjaž Percf, g, Nicola Perra h , Marcel Salathé i j, Dawei Zhaok
a Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Engineering Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, 816-8580, Japan
b Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON N2L 3G1, Canada
c Department of Mathematics, School of Natural Sciences, Shiv Nadar University, India
d International Prevention Research Institute, 95 Cours Lafayette, 69006 Lyon, France e Department of Economics and Management, University of Pisa, Italy
f Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, University of Maribor, Koroška cesta 160, SI-2000 Maribor, Slovenia
g Center for Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Maribor, Krekova 2, SI-2000 Maribor, Slovenia
h Centre for Business Network Analysis, Greenwich University, Park Raw, SE10 9LS, London, United Kingdom
i School of Life Sciences, EPFL, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland
j School of Computer and Communication Sciences, EPFL, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland
k Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Computer Networks, Shandong Computer Science Center (National Supercomputer Center in Jinan), Jinan 250014, China
https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.09010
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.09010
‘COVID-19 Open Research Dataset Challenge (CORD-19)’
An AI challenge with AI2, CZI, MSR, Georgetown, NIH & The White House
Allen Institute For AI and 8 collaborators
https://web.archive.org/web/20221001081548/https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/allen-institute-for-ai/CORD-19-research-challenge